The 10 best metrics for talent acquisition
Why use metrics for talent acquisition?
In an era where talent is a key driver of organisational success, understanding and optimising your talent acquisition processes can provide a significant competitive edge. Metrics for talent acquisition help organisations measure the efficiency, effectiveness, and overall impact of their recruitment processes. By monitoring these metrics, you can identify areas for improvement, streamline processes, and ensure you're attracting and retaining the best talent.
The top 10 metrics for talent acquisition
1. Time to hire
Time to hire measures the duration between when a job requisition is opened and when an offer is accepted. It is essential because it indicates the efficiency of your hiring process.
- How time to hire is calculated: Calculate by subtracting the date the job requisition was opened from the date the offer was accepted.
- What tools can be used to get time to hire data: Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) like Greenhouse, Lever, or Jobvite.
- What average, good, and best in class look like for time to hire:
- Average: 30-45 days
- Good: 20-30 days
- Best in class: 10-20 days
2. Cost per hire
Cost per hire evaluates the total expense involved in hiring a new employee, which includes advertising costs, recruiter salaries, referral bonuses, and other related expenses. It ensures financial efficiency in the hiring process.
- How cost per hire is calculated: Sum all the hiring-related expenses and divide by the number of hires.
- What tools can be used to get cost per hire data: HR software like Workday, BambooHR, or Zoho Recruit.
- What average, good, and best in class look like for cost per hire:
- Average: £3,000-£4,000
- Good: £2,000-£3,000
- Best in class: Less than £2,000
3. Quality of hire
Quality of hire measures the value that new hires bring to the organisation, typically assessed through performance ratings, retention rates, and feedback from managers.
- How quality of hire is calculated: Commonly measured through performance evaluations, retention rates, and feedback during the first year.
- What tools can be used to get quality of hire data: Performance management tools like Lattice, 15Five, or Reflektive.
- What average, good, and best in class look like for quality of hire:
- Depends on your scoring system, but generally, improved performance ratings within the first year indicate a good quality of hire.
4. Offer acceptance rate
Offer acceptance rate gauges the percentage of job offers that are accepted by candidates. A high rate suggests competitive offers and effective candidate matching.
- How offer acceptance rate is calculated: Divide the number of accepted offers by the total number of offers made, then multiply by 100.
- What tools can be used to get offer acceptance rate data: ATS platforms like Greenhouse, Lever, or Jobvite.
- What average, good, and best in class look like for offer acceptance rate:
- Average: 75-85%
- Good: 85-90%
- Best in class: 90-95%
5. Candidate experience
Candidate experience assesses the overall experience of candidates throughout the recruitment process, from application to onboarding.
- How candidate experience is calculated: Typically measured through surveys sent to candidates after the hiring process concludes.
- What tools can be used to get candidate experience data: Survey tools like SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or hiring platforms with built-in feedback systems.
- What average, good, and best in class look like for candidate experience:
- Average: Mixed feedback
- Good: Generally positive feedback
- Best in class: Highly positive feedback with actionable insights for improvement
6. Source of hire
Source of hire identifies which channels (e.g., job boards, social media, referrals) are the most effective in attracting candidates. This metric helps optimise recruitment strategies by focusing on the most productive sources.
- How source of hire is calculated: Track the number of hires originating from each source and calculate the percentage share each source contributes.
- What tools can be used to get source of hire data: ATS platforms like Greenhouse, Lever, or analytics tools like Google Analytics.
- What average, good, and best in class look like for source of hire:
- Varies widely by industry but focusing on sources which consistently yield quality candidates.
7. Recruitment funnel effectiveness
Recruitment funnel effectiveness measures the conversion rates at each stage of the recruitment process, helping to identify bottlenecks and improve the flow from application to hire.
- How recruitment funnel effectiveness is calculated: Track the number of candidates that move from one stage to the next, calculate conversion rates for each stage.
- What tools can be used to get recruitment funnel effectiveness data: ATS platforms like Greenhouse, Lever.
- What average, good, and best in class look like for recruitment funnel effectiveness:
- Average: Conversion rates are lower at the initial stages, higher at the final stages.
- Good: 20-30% conversion between stages.
- Best in class: 30-50% conversion between stages.
8. Candidate diversity
Candidate diversity tracks the diversity of candidates throughout the hiring process, ensuring fair representation of different demographics.
- How candidate diversity is calculated: Collect demographic data voluntarily provided by candidates, assess the composition of your applicant pool, shortlists, and hires.
- What tools can be used to get candidate diversity data: HR software like Workday, BambooHR, and diversity-focused platforms like Diversio.
- What average, good, and best in class look like for candidate diversity:
- Goals vary by organisation; the key is to consistently work towards improving representation.
9. Hiring manager satisfaction
Hiring manager satisfaction measures the satisfaction of hiring managers with the recruitment process and the suitability of candidates presented to them.
- How hiring manager satisfaction is calculated: Conduct surveys or interviews with hiring managers post-hire.
- What tools can be used to get hiring manager satisfaction data: Survey platforms like SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or performance management tools.
- What average, good, and best in class look like for hiring manager satisfaction:
- Average: Mixed feedback.
- Good: Generally positive feedback with minor improvement areas.
- Best in class: Highly positive feedback with clear indications of a streamlined process.
10. Employee retention rate
Employee retention rate tracks how long new hires stay with the organisation, providing insights into the success of the hiring and onboarding process.
- How employee retention rate is calculated: Divide the number of employees who remain after a certain period by the total number of hires in that period, then multiply by 100.
- What tools can be used to get employee retention rate data: HR software like Workday, BambooHR, or ADP.
- What average, good, and best in class look like for employee retention rate:
- Average: 70-80% (one-year retention)
- Good: 80-90% (one-year retention)
- Best in class: Over 90% (one-year retention)
How to track metrics for talent acquisition
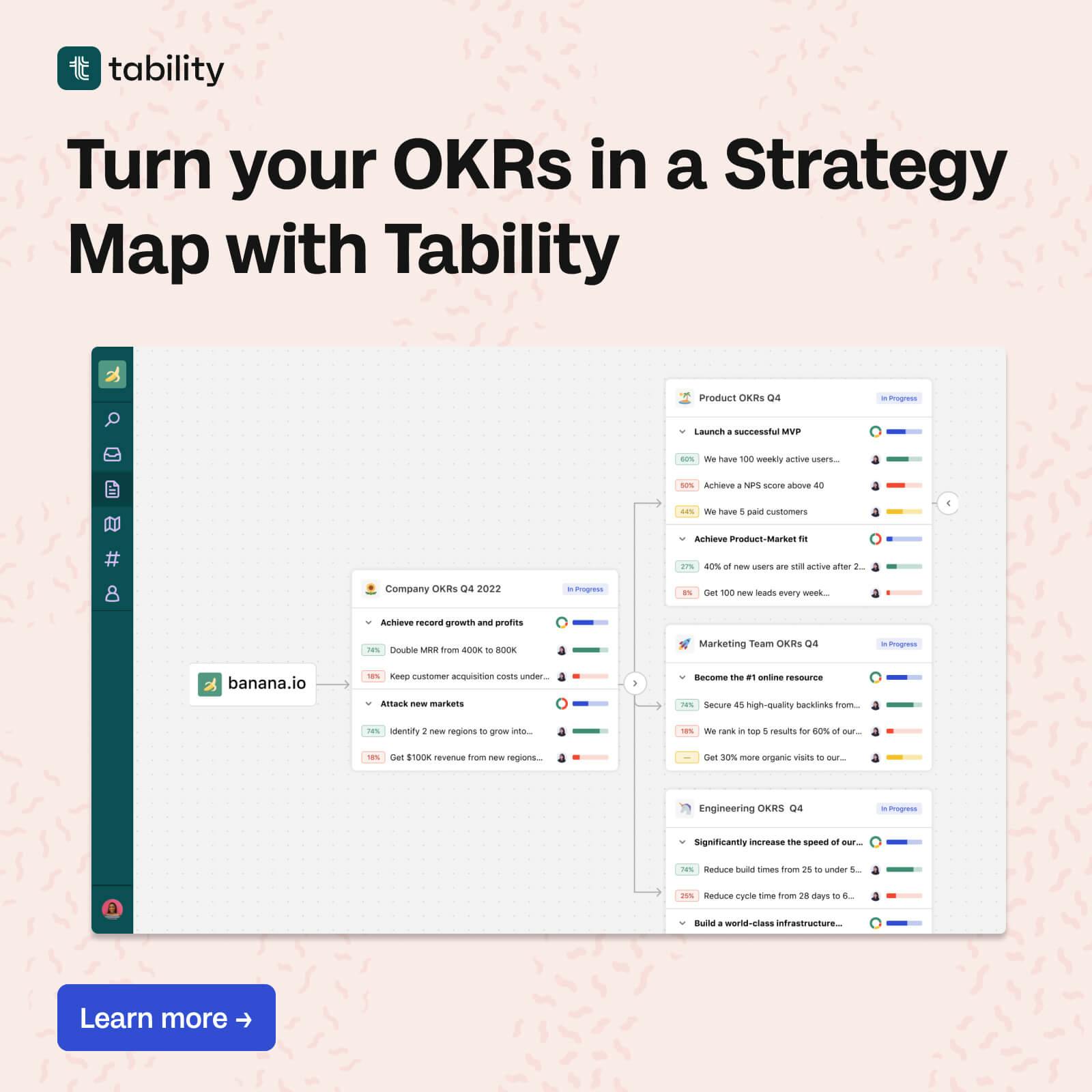
Tracking metrics for talent acquisition can be time-consuming, but it is crucial for improving your recruitment processes. Using a goal-tracking tool like Tability can save you time and help your team stay focused on the right metrics to improve. Tability allows you to set clear goals, monitor progress, and make data-driven decisions based on real-time insights.
Whether you use Tability or other specialised ATS platforms and HR software, ensure that your tools are integrated, accessible, and user-friendly. Regularly review and analyse your metrics to identify trends, pinpoint areas needing improvement, and celebrate successes.
FAQ
Q: What is the most important talent acquisition metric? A: The most important metric can vary based on your organisational goals, but commonly, time to hire, quality of hire, and cost per hire are considered highly crucial as they directly impact the efficiency, effectiveness, and financial health of the recruitment process.
Q: How often should we review talent acquisition metrics? A: Ideally, talent acquisition metrics should be reviewed monthly to ensure ongoing optimisation. However, some organisations may choose to review them quarterly or biannually based on their specific needs and resource availability.
Q: Can tracking too many metrics be counterproductive? A: Yes, tracking too many metrics can lead to data overload and distract from focusing on critical areas. It’s important to prioritise and focus on the most impactful metrics that align with your recruitment goals.
Q: How can we improve our candidate experience metric? A: Improving candidate experience involves clear communication, providing timely updates, ensuring a seamless interview process, and offering constructive feedback regardless of the hiring outcome. Regularly collecting and acting on candidate feedback is also key.
Q: Why is candidate diversity an important metric? A: Candidate diversity ensures that you are attracting a wide range of talent and promoting a inclusive work environment, which can enhance creativity, innovation, and overall organisational performance.